What is VPN ?
This is most common question asked in majority of technical support engineer’s interview or Desktop Support Engineer’s Interview , today I promise , In this article you will get in depth information about VPN.
Lets understand VPN in simple language first : 🙂
Imagine the internet is a public street. When you go online without a VPN, it’s like walking down on that public street with no clothes and face mask. Anyone can see your face where you go, what you do, and what you buy.
A VPN is like putting on or wearing a coat with mask. It hides you from others, so they can’t see where you’re going or what you’re doing. It keeps you safe and private online.
I hope you got basic idea about VPN.
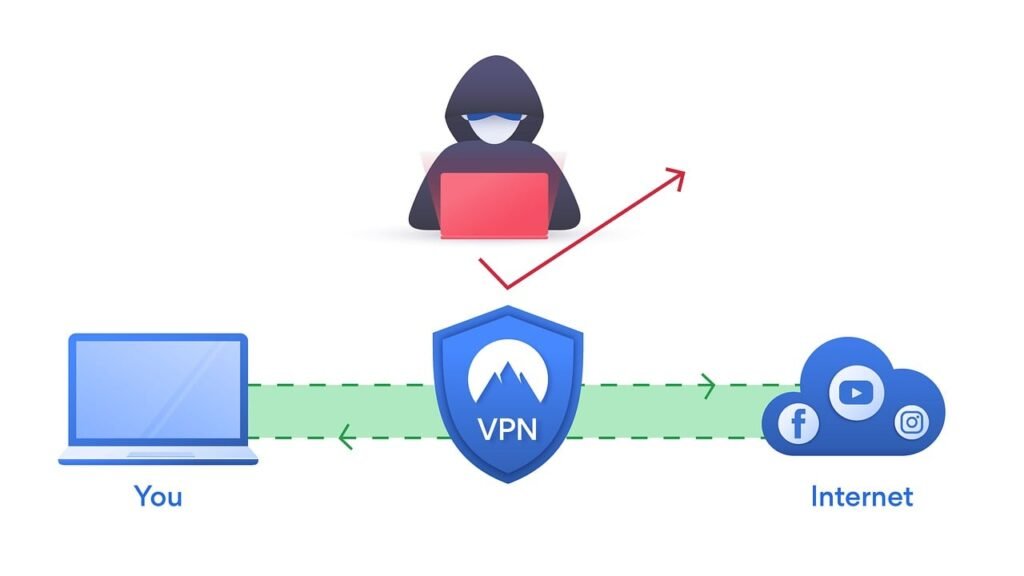
VPN creates a secret tunnel between your device(example laptop) and the internet, so no one can see what you’re doing inside.
Now , Lets Understand definition of VPN in professional way for job interview’s :
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the internet. It works by establishing a secure tunnel between your device and a remote server, masking your IP address and encrypting your data. This encrypted “tunnel” masks your IP address, making it difficult for third parties to track your online activities and intercept your information.
How Does a VPN Work ?
- Connection Establishment: When you connect to a VPN server, a secure, encrypted tunnel is created between your device and the server.
- Data Encryption: All your internet traffic is encrypted before it’s sent through the tunnel.
- IP Masking: Your device receives a new IP address from the VPN server, hiding your real location. Your device gets a new address (like a fake ID) from the VPN server. This hides your real location.
- Secure Data Transmission: All your internet traffic goes through this secret tunnel, encrypted so no one can snoop on it. The encrypted data travels through the tunnel to the VPN server and then to its destination.
How to use a VPN ?
- Choose a VPN provider: Research reputable VPN providers and select a plan that suits your needs.
- Download and install the VPN app: Download the VPN app from the provider’s website or app store. (Note : Take proper precaution don’t install any ordinary app or new app which is not from reputed organization there are many fake VPN App which can make you fool).
- Create an account: Sign up for an account with the VPN provider.
- Connect to a server: Choose a server location and connect to it through the VPN app.
- Start browsing securely: Once connected , your internet traffic will be encrypted and routed through the VPN server.
Why To Use a VPN ? and Key benefits of using a VPN
Privacy: Hide your online activity from your internet provider, government, and hackers.
VPN Hides your IP address and encrypts your internet traffic, making it difficult for anyone to track your online activities.A VPN masks your IP address, making it difficult for websites, ISPs, and governments to track your online activities.
Security: Protects your data from hackers and cybercriminals by encrypting your connection , Protect your sensitive information, like passwords and bank details, from being stolen.VPN Increases security By encrypting your internet traffic, a VPN protects your sensitive data from hackers and cybercriminals.
Access to Blocked Content(Access to geo-restricted content): Allows you to bypass censorship and allow you to access content that may be blocked in your region. You can Watch movies or TV shows that are only available in certain countries.
Public Wi-Fi security: Public Wi-Fi networks can be vulnerable to security threats. A VPN encrypts your connection, protecting your data from potential hackers. VPN Encrypts your connection on public Wi-Fi networks, protecting your data from potential threats. Use public Wi-Fi safely without worrying about hackers stealing your data.
In simple terms, a VPN is like a personal bodyguard for your online activities, keeping you safe and anonymous.
Choosing the Right VPN
When selecting a VPN, consider the following factors:
Security Protocols: Strong encryption protocols like OpenVPN, WireGuard, and IKEv2/IPsec ensure robust security.
Server Network: A larger network of servers provides more options for connecting to different locations.
No-Logs Policy: A reputable VPN provider should adhere to a strict no-logs policy, meaning they don’t store any information about your online activities.
Speed and Performance: A fast VPN connection is essential for smooth browsing and streaming.
Customer Support: Reliable customer support is crucial for resolving any issues or questions.
Common Misconceptions About VPN
1.Misconceptions About VPN is VPNs Make You Anonymous : While VPNs can enhance your privacy, they don’t make you completely anonymous. It’s important to practice good online security habits, such as using strong passwords and avoiding suspicious websites.
2.Misconceptions About VPN is VPNs Are Only for Hackers: Not only hacker’s , VPNs are used by a wide range of people, including individuals, businesses, and organizations, for various purposes.
Security Best Practices
- Choose a Reputable VPN Provider: Research and select a provider with a strong track record in security and privacy.
- Strong Password and Two-Factor Authentication: Use a unique, complex password for your VPN account and enable two-factor authentication for added security.
- Regularly Update the VPN App: Keep your VPN app up-to-date to benefit from the latest security patches and features.
- Be Cautious of Free VPNs: Free VPNs may compromise your privacy by selling your data or injecting ads.
- Use a Kill Switch: A kill switch automatically disconnects your internet connection if the VPN fails, preventing any unencrypted traffic from leaking.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi Without a VPN: Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them easy targets for hackers. Always use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi.
- Be Aware of Phishing Attacks: Be vigilant for phishing emails or websites that may try to steal your VPN credentials.
Diving Deeper into VPNs: Technical Aspects and Security Best Practices
Understanding the Technicalities
Encryption:
Symmetric Encryption: A single key is used for both encryption and decryption. While fast, it requires secure key exchange.
Asymmetric Encryption: Uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This is commonly used for secure communication over the internet.
Tunneling Protocols:
OpenVPN: A popular open-source protocol known for its security and flexibility.
WireGuard: A newer, faster protocol that prioritizes simplicity and performance.
IKEv2/IPsec: A robust protocol often used in corporate environments.
VPN Types:
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol): An older protocol, less secure than modern options.
L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol/IPsec): Offers better security than PPTP but can be slower.
SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol): A Microsoft protocol that can bypass firewalls.
Real-World Use Cases and Where VPN is used in Real Time :
Remote Work: VPNs enable secure remote access to company networks, allowing employees to work from anywhere.
Online Privacy: By masking your IP address and encrypting your traffic, VPNs protect your online privacy from snooping.
Geo-Restricted Content: VPNs allow you to bypass geo-restrictions and access content that may be blocked in your region.
Secure Public Wi-Fi: VPNs provide a secure connection when using public Wi-Fi hotspots, protecting your data from potential threats.
Online Gaming: VPNs can improve gaming performance by reducing latency and avoiding DDoS attacks.
What are VPN Encryption Protocols
VPN encryption protocols are the backbone of secure, private internet connections. They determine the level of security and performance of a VPN. Here are some of the most popular protocols:
OpenVPN
Security: Strong encryption and authentication.
Flexibility: Can be configured for various security levels and performance needs.
Drawback: Can be relatively slow compared to newer protocols.
WireGuard
Speed: Known for its high speed and low latency.
Simplicity: A relatively simple protocol to implement and maintain.
Security: Provides strong encryption and authentication.
IKEv2/IPsec
Security: Offers robust security features, including perfect forward secrecy.
Reliability: Handles network changes and device reconnections well.
Complexity: Can be more complex to configure than other protocols.
Choosing the Right Protocol
The best protocol for you depends on your specific needs:
Prioritize security: OpenVPN or IKEv2/IPsec are excellent choices.
Need high speed and simplicity: WireGuard is a great option.
Balancing security and performance: IKEv2/IPsec is a good compromise.
Remember:
Protocol Strength: A strong protocol is essential, but it’s only as good as its implementation.
VPN Provider’s Infrastructure: The VPN provider’s network infrastructure, server locations, and overall security practices play a significant role in your online security.
Regular Updates: Keep your VPN software and device operating systems up-to-date to address security vulnerabilities.
By understanding these protocols and making informed choices, you can significantly enhance your online privacy and security.
Future Trends in VPN Technology
As technology continues to evolve, so too does VPN technology. Here are some of the future trends we can expect:
1. AI-Powered VPNs:
Intelligent Routing: AI can analyze network conditions and automatically route traffic through the most secure and efficient servers.
Enhanced Security: AI can detect and mitigate threats in real-time, providing advanced protection against cyberattacks.
2. Quantum-Resistant VPNs:
Post-Quantum Cryptography: As quantum computing advances, VPNs will need to adopt quantum-resistant encryption algorithms to safeguard data.
3. Multi-Hop VPNs:
Increased Privacy: By routing traffic through multiple servers, multi-hop VPNs can further obfuscate user activity and make it harder to track.
Enhanced Security: Multiple layers of encryption can provide additional protection against attacks.
4. Mesh Networks:
Decentralized VPNs: Mesh networks can create peer-to-peer VPN connections, making it more difficult for attackers to identify and compromise the network.
5. Zero-Trust VPNs:
Strict Access Controls: Zero-trust VPNs require continuous verification of user identity and device security before granting access to network resources.
Enhanced Security: This approach reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
As technology continues to advance, VPNs will play an increasingly important role in protecting our online privacy and security. By staying informed about the latest trends and best practices, you can ensure that you’re well-protected in the digital age.
In today’s digital age, a VPN is an essential tool for protecting your online privacy and security. By understanding how VPNs work and choosing the right provider, you can safeguard your digital identity and enjoy a more secure online experience.
Happy Learning 🙂
best VPN for privacy, fastest VPN for streaming, most secure VPN for gaming, cheap VPN with good security, VPN for torrenting, VPN for China, VPN for Netflix, OpenVPN VPN, WireGuard VPN, IKEv2 VPN, no-log VPN, kill switch VPN, split tunneling VPN, VPN for remote work, VPN for public Wi-Fi, VPN for travelers, VPN for students, VPN for businesses, secure VPN, private VPN, anonymous VPN, fast VPN, reliable VPN, easy-to-use VPN, affordable VPN, best VPN for Mac, best VPN for Windows, best VPN for Android, best VPN for iOS, VPN for routers, VPN for smart TVs, VPN for gaming consoles, VPN for cryptocurrency, VPN for email privacy, VPN for social media, VPN for online banking, VPN for online shopping, VPN for journalists, VPN for activists, VPN for whistleblowers, how to use a VPN, how to choose a VPN, VPN benefits, VPN risks, VPN legality, VPN future, VPN news,best VPN for privacy, fastest VPN for streaming, most secure VPN for gaming, cheap VPN with good security, VPN for torrenting, VPN for China, VPN for Netflix, OpenVPN VPN, WireGuard VPN, IKEv2 VPN, no-log VPN, kill switch VPN, split tunneling VPN, VPN for remote work, VPN for public Wi-Fi, VPN for travelers, VPN for students, VPN for businesses, secure VPN, private VPN, anonymous VPN, fast VPN, reliable VPN, easy-to-use VPN, affordable VPN, best VPN for Mac, best VPN for Windows, best VPN for Android, best VPN for iOS, VPN for routers, VPN for smart TVs, VPN for gaming consoles, VPN for cryptocurrency, VPN for email privacy, VPN for social media, VPN for online banking, VPN for online shopping, VPN for journalists, VPN for activists, VPN for whistleblowers, how to use a VPN, how to choose a VPN, VPN benefits, VPN risks, VPN legality, VPN future, VPN news,best VPN for privacy, fastest VPN for streaming, most secure VPN for gaming, cheap VPN with good security, VPN for torrenting, VPN for China, VPN for Netflix, OpenVPN VPN, WireGuard VPN, IKEv2 VPN, no-log VPN, kill switch VPN, split tunneling VPN, VPN for remote work, VPN for public Wi-Fi, VPN for travelers, VPN for students, VPN for businesses, secure VPN, private VPN, anonymous VPN, fast VPN, reliable VPN, easy-to-use VPN, affordable VPN, best VPN for Mac, best VPN for Windows, best VPN for Android, best VPN for iOS, VPN for routers, VPN for smart TVs, VPN for gaming consoles, VPN for cryptocurrency, VPN for email privacy, VPN for social media, VPN for online banking, VPN for online shopping, VPN for journalists, VPN for activists, VPN for whistleblowers, how to use a VPN, how to choose a VPN, VPN benefits, VPN risks, VPN legality, VPN future, VPN news,
Leave a Reply